- Africa acquired loans price $4.6 billion from China final yr, a rise from what economies throughout the continent acquired in 2022.
- This quantity is, nevertheless, a far cry from Beijing’s large infrastructure financing witnessed earlier than the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Beijing will host African leaders for the Discussion board on China-Africa Cooperation between September 4th-Sixth.
A complete of 9 nations in Africa acquired Chinese language loans price $4.6 billion final yr, a rise from what economies throughout the continent acquired in 2022. Nonetheless, this quantity is a far cry from Beijing’s large infrastructure financing that was witnessed earlier than the Covid-19 pandemic.
The brand new statistics from the Boston College International Improvement Coverage Centre come simply days earlier than Beijing hosts African leaders for the Discussion board on China-Africa Cooperation, scheduled for September 4th-Sixth.
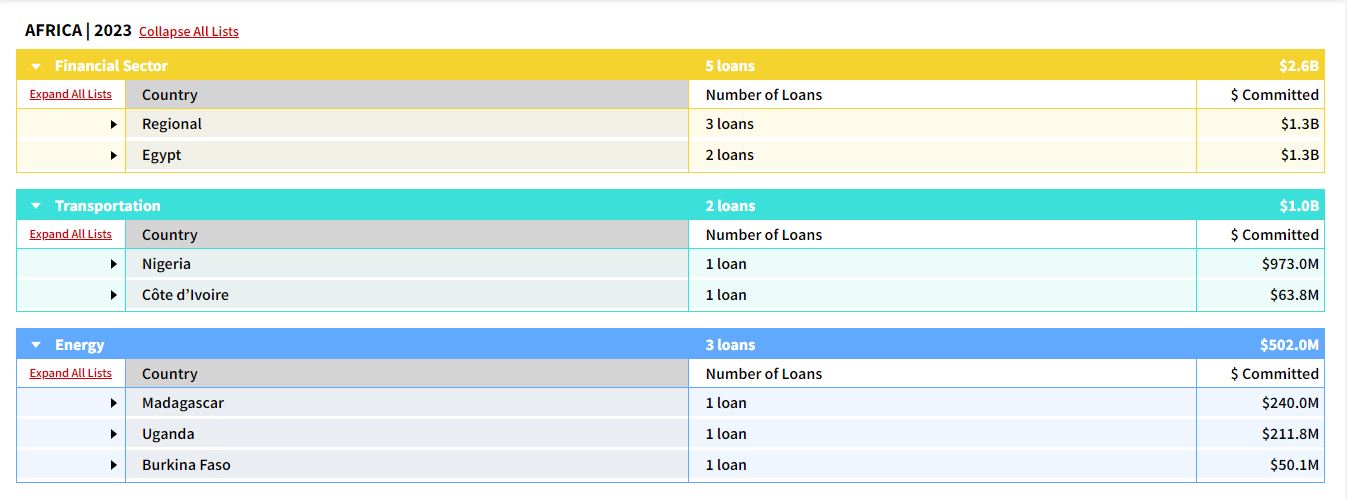
In 2023, lenders from China processed roughly 13 loans concentrating on numerous tasks throughout the continent with the most important beneficiary being gamers within the monetary providers business who acquired loans price $2.6 billion.
Different sectors in Africa that acquired vital funding from Chinese language establishments have been state-owned investments in transport at $1 billion, vitality at $502 million, Data Communication and Know-how (ICT) at $396.5 million in addition to a non-energy mining venture in Eritrea that obtained $85.8 million in funding from Beijing.
China directs extra loans by means of multilateral lenders
In accordance with Boston analysts, over half of the monies from China to Africa have been processed by means of multilateral lenders, a shift from an earlier development the place the funding went on to governments.
As an example, within the monetary providers business, the state-owned China Improvement Financial institution (CDB) channeled $400 million in loans to help Small and Micro Enterprises (SMEs) below a venture run by multilateral lender Afreximbank. This financing means that it’s going to go to beneficiaries unfold throughout the continent as Afreximbank rolls out SME help initiatives.
Moreover, the report exhibits that the Export-Import Financial institution of China (CHEXIM) supplied $600 million in credit score to facilitate commerce and monetary partnerships below the PRC Assist Initiative. To spice up commerce finance in Africa, CHEXIM additional signed a mortgage of $300 billion with the Africa Finance Company (AFC) in 2023, too.
Within the transport sector, Africa’s most populous nation Nigeria was the most important winner after securing a $973 million mortgage from the CDB for the development of the nation’s first customary gauge railway line. The 1,400km railway will traverse the states of Lagos, Oyo, Ogun, Kaduna, linking them to the West African nation’s industrial hub of Kano. This funding will even prolong the Kaduna-Kano railway part, which is roughly 200km.
One other huge winner in Africa’s transport business was Côte d’Ivoire, which secured $$63.8 million in credit score from the Financial institution of China (BoC) for the development of the 50km Tioroniaradougou–Dikodougou Highway. This mortgage settlement additionally supplied further finance for rehabilitation and asphalting works within the West African nation.
Madagascar, Uganda, and Burkina Faso safe financing in vitality
In 2023, Chinese language investments within the vitality business in Africa totaling $502 million went to 3 nations: Madagascar, Uganda, and Burkina Faso. In Madagascar, the CHEXIM disbursed $240 million to arrange of the 64MW Ranomafana Hydropower Plant, in Ikopa River.
For Uganda, the third part of electrification of commercial parks in Jinja, Njeru, Masese, Kasese, Ishaka areas, which can run for a mixed 118.5km, acquired $211.8 million from CHEXIM within the yr below overview.
Moreover, Burkina Faso acquired $50.1 million in mortgage from CHEXIM for the event of a 25MW Donsin solar energy plant. With this inexperienced vitality funding, Burkina Faso goals to make sure vitality safety at Donsin airport and step up the nation’s vitality manufacturing capability from the present 714.4MW.
At present, at 92MWp, Burkina Faso is the main producer of photo voltaic vitality within the area, main neighbours Mauritania (84MWp), Ivory Coast (37MWp), and Mali (50MWp). The nation’s Donsin solar energy plant is estimated to take 15 months to construct.
Information from the Boston College International Improvement Coverage Middle exhibits that China’s CHEXIM was the only financier of ICT tasks, channeling $249 million to Angola’s Nationwide Broadband Venture and an extra $147.5 million to the fifth part of Uganda’s nationwide information transmission spine infrastructure/ e-government infrastructure venture.
Angola is at the moment constructing a 2,000-km land optical cable in Angola and a submarine line linking the enclave of Cabinda below its nationwide broadband venture which goals at upgrading the nation’s telecommunications infrastructure.
Below the non-energy mining focus space, the info exhibits an alliance of CHEXIM and different lenders from China dedicated an $85.8 million mortgage to Eritrea’s Asmara Copper-Chilly Polymetallic Venture.
Learn additionally: Kenya’s Debt Misery Risk to its Lengthy-Time period Improvement Agenda -Consultants
Chinese language loans in 2023 mirror a cautious stance from Beijing
General, China’s lending to Africa in 2023 noticed a notable shift, reflecting a extra cautious and strategic method in comparison with the early years of the Belt and Highway Initiative (BRI). Below President Xi Jinping, the BRI initially led to a surge in Chinese language loans to Africa, with annual quantities exceeding $10 billion.
This aggressive lending technique was a part of China’s broader ambition to boost international infrastructure connectivity. Nonetheless, the appearance of the COVID-19 pandemic and China’s subsequent financial slowdown resulted in a big discount in loans to the continent.
This decline was additional exacerbated by the protracted debt restructuring processes in some African nations, elevating issues in regards to the sustainability of such monetary engagements.
Critics have lengthy accused China of ensnaring African nations in so-called “debt traps,” the place the big sums owed to Chinese language corporations allegedly place African governments below Beijing’s financial and political affect.
Nonetheless, proof means that each events are engaged in a mutually helpful partnership, with African nations leveraging Chinese language loans for crucial infrastructure growth.
In a big growth, the lending patterns in 2023 marked a departure from the earlier traits, with a greater than three-fold improve in loans in comparison with 2022. This surge signifies China’s renewed curiosity in African markets, albeit with a extra calculated method.
In accordance with a research by Boston College’s International Improvement Coverage Centre, China is now specializing in minimizing dangers related to extremely indebted economies. The report means that Beijing is experimenting with a brand new lending technique aimed toward reaching a extra sustainable equilibrium.